Selecting penetration enhancers, for transdermal delivery
To overcome the skin barrier properties, many strategies exist, among which the use of chemical penetration enhancers, that modify the stratum corneum through different mechanisms of interaction with the skin structure.
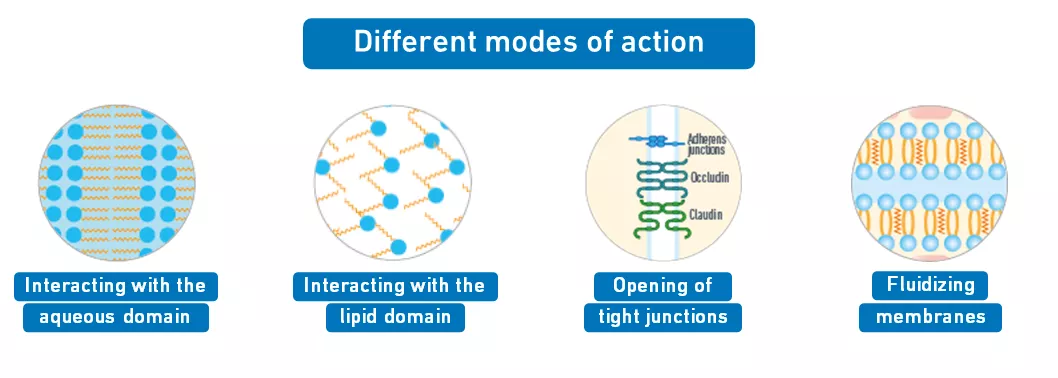
Penetration enhancers with different modes of action
-
Enables skin penetration with no effect on skin lamellar structure
-
Solvent
-
Reversibly opens tight junctions
-
No modification of the horny layer
-
Liquid surfactant HLB = 12
-
Enables skin penetration with no effect on skin lamellar structure
-
Solvent
-
Reversibly opens tight junctions
-
No modification of the horny layer
-
Liquid surfactant HLB = 12
-
Enables drug penetration with slight modification of the lipid domain of the skin
-
Liquid co-surfactant HLB = 3
-
Medium chain fatty acid esters (C8) of propylene glycol known to enhance skin penetration
-
Liquid co-surfactant HLB = 5
-
Medium chain fatty acid esters (C8) of propylene glycol known to enhance skin penetration
-
Liquid co-surfactant HLB = 6
-
Medium chain fatty acid esters (C12) of propylene glycol known to enhance skin penetration
-
Liquid co-surfactant HLB = 3
-
Medium chain fatty acid esters (C12) of propylene glycol known to enhance skin penetration
-
Liquid co-surfactant HLB = 5
Evaluating skin permeation with in vitro release test (IVRT) and in vitro permeation test (IVPT)
In vitro methods exist to assess the drug penetration through the skin: IVRT uses synthetic membranes while IVPT uses animal or human skin.
Rigorous protocols need to be developed to ensure the reliability of the results. Detailed information is given in our joint webinar with Teledyne Hanson provider of Franz cells. Gattefossé has developed standard protocols to evaluate skin penetration properties of our excipients in formulations.


