Patch, for controlled skin drug delivery
Adhesive patches are solid unit drug dosage forms, fixed to the skin to deliver a specific dose of medication within a given time. Patches provide significant advantages with a safe, continuous and controlled drug delivery of effective therapeutic dose, improved bioavailability and improved patient compliance.
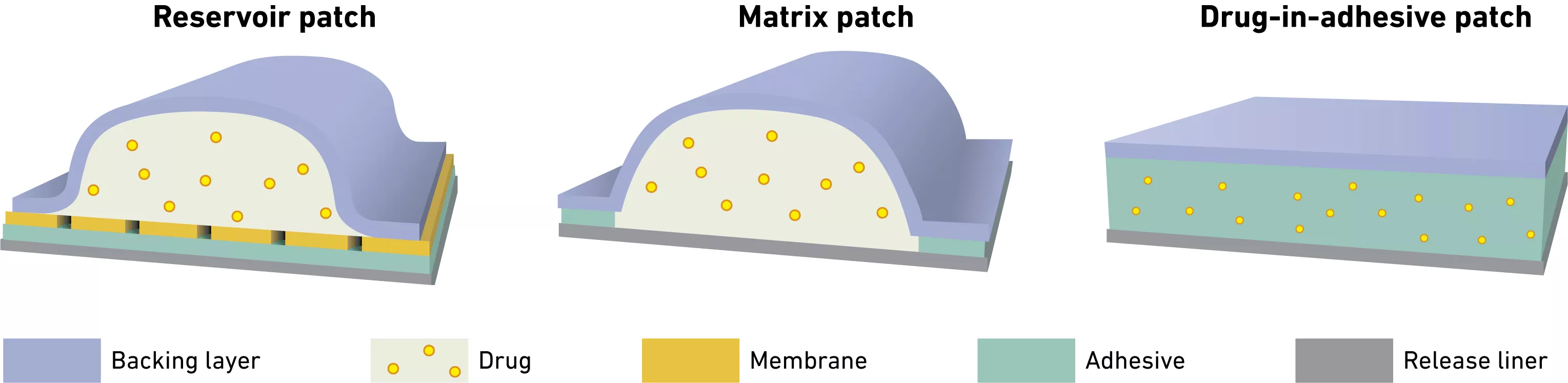
Understanding patch composition for effective transdermal drug delivery
Composition includes a mixture of API and excipients, a skin adhesive, a controlled-release system,
and structural films. Main excipients include drug solubilizer and skin penetration enhancer and rheology modifier of the adhesive matrix, which can also impact the drug solubility. Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) performance is driven by a suitable viscoelasticity behavior, which can be impacted significantly when the PSA is blended with drug and excipient(s), especially in a drug-in-adhesive patch configuration.
Multi-functional excipients for enhanced patch effectiveness
In patches, our excipients exert different functionalities, such as drug solubilizer, skin penetration enhancer and adhesive plasticizer.
|
Gattefossé excipient |
Solubilizer |
Penetration enhancer |
Plasticizer |
|
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
|
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
|
✓ |
|
✓ |
|
|
✓ |
|
|
|
|
✓ |
|
|
|
|
✓ |
|
|
|
|
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
|
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
|
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
|
✓ |
|
✓ |
|
|
✓ |
|
✓ |
|
|
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |

In this webinar, experts from DuPont™ Liveo™ Healthcare, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University and Gattefossé will discuss:
-
Types of patches, illustrated with market examples
-
Excipient functionality, with particular emphasis on solubilizers, penetration enhancers and adhesives, and their interactions
-
Case studies with anti-inflammatories and pain management drugs in drug-in-adhesive and reservoir patches